
So, what exactly is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? AI core concepts involve machines, particularly computer systems, simulating human intelligence processes. These processes encompass learning (gaining information and rules for using it), reasoning (applying rules to reach conclusions), and self-correction.
AI’s journey began in the mid-20th century but has seen exponential growth and development in recent years. From early conceptual theories and basic computational models, AI has evolved into sophisticated systems capable of performing complex tasks across diverse domains.
Before we go deeper, here’s the simplest way to think about AI core concepts:
- AI is the big umbrella.
- Machine learning is how many AI systems learn from data.
- Neural networks are one family of machine learning models.
- Deep learning is a type of neural network with many layers, used when patterns are too complex for simpler models.
Everything I’ve shared here—and more—is in my book, available on Amazon. Click the link if you’re ready to take the next step.
Importance of AI Core Concepts in Today’s World
AI is more than a buzzword; it’s transforming industries and shaping the future. Picture healthcare without AI-driven diagnostics or finance without AI-enhanced fraud detection. These technologies streamline processes, enhance accuracy, and inspire hope for a more efficient and innovative future.
In McKinsey’s 2024 global survey, 65% of organizations said they were regularly using generative AI in at least one business function, nearly double the share from just ten months earlier, showing how fast these core concepts are moving into everyday operations.
AI is more present in your everyday life than you might realize. It’s behind the recommendations on your favorite streaming service, the smart assistant you talk to, and even the algorithms that filter spam from your inbox. AI is an integral part of the digital fabric, simplifying and enriching our lives, making us more connected and aware of its impact.
Empower Yourself with AI Knowledge
- Machine Learning (ML): This subset of AI core concepts involves computers learning from data without being explicitly programmed.
- Neural Networks: These computer systems mimic the human brain’s network of neurons, recognizing patterns and interpreting data to emulate human cognition.
- Deep Learning: This specialized form of ML employs neural networks with numerous layers (hence “deep”) to analyze various data factors.
Understanding artificial intelligence terms is crucial because they highlight the layers and complexities within AI. Machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning uniquely affect how AI functions and evolves.
Core Components of AI
AI can feel like a black box until you break it into parts. Machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning aren’t three separate trends—they’re layers of the same story. When you understand how each layer works (and what it’s good at), AI stops sounding like hype and starts looking like a system you can evaluate.
Machine Learning
Machine learning is the heart of AI. The technique allows AI systems to learn from data and improve over time. Think of it as teaching a computer how to perform a task by feeding it large amounts of data and letting it learn from patterns and correlations.
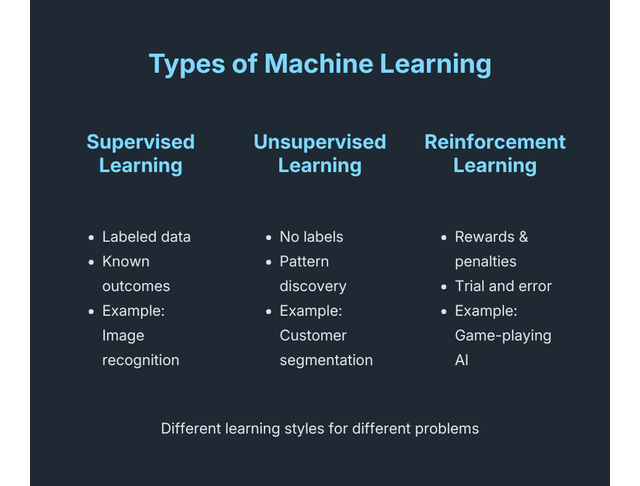
There are three principal kinds of machine learning:
- Supervised Learning: Here, you train the system using a labeled dataset, which includes input-output pairs. For example, teaching a machine to recognize cats by showing it thousands of labeled cat images, where each image is ‘labeled’ with the information that it contains a cat.
- Unsupervised Learning: In this approach, you give the system data without explicit instructions on how to use it. The system identifies patterns and relationships within the data. A typical example is a clustering algorithm, which groups similar data points.
- Reinforcement Learning: This method involves training a system through trial-and-error. The system learns to make decisions by receiving rewards or penalties based on its actions, much like training a pet.
Recommendation engines in e-commerce use machine learning to recommend products based on your browsing history and purchase history.
Neural Networks
Neural networks are the foundation of deep learning. They feature interconnected nodes, or neurons, that process data in layers. The design draws inspiration from the human brain, where each neuron sends data to multiple other neurons, forming a complex network of interactions.
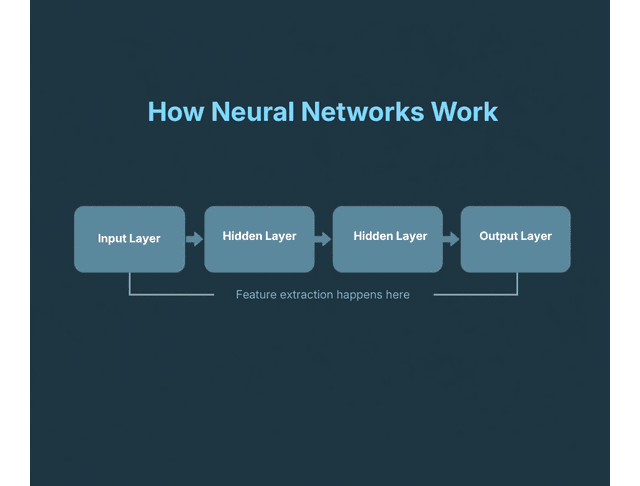
A neural network typically consists of:
- Input Layer: Receives the initial data.
- Hidden Layers: Perform computations and extract features from the data. Depending on the task’s complexity, these layers can range from 1 to hundreds.
- Output Layer: Delivers the absolute projection or category.
Neural networks are powerful tools for image and speech recognition. For example, they enable smartphones to recognize voice commands and for social media platforms to tag friends in photos automatically.
Deep Learning
Deep learning takes neural networks to the next level. Its standards use multiple layers of neurons to handle vast amounts of data and detect complex patterns that simpler models might overlook.
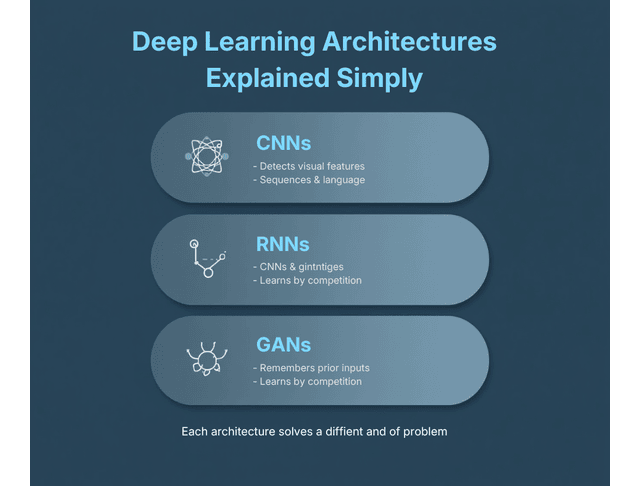
There are several architectures in deep learning, each suited for different tasks:
- Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): Ideal for image processing, CNNs can detect features such as edges, textures, and objects.
- Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs): You use these for sequential data, such as time series or natural language processing. RNNs retain information from previous inputs in their memory cells, making them suitable for tasks like language translation.
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): GANs consist of two networks—the generator and the discriminator—that compete against each other. This competition helps the generator create highly realistic data, such as deepfake images or artwork.
Deep learning has revolutionized fields such as autonomous driving, where vehicles use it to interpret and respond to their surroundings in real time. It also powers many of the tools writers already use every day, from smart research assistants to drafting aids; if you want to see how that works in your own workflow, our Artificial Intelligence for Writers guide walks through concrete examples in plain language.
Practical Applications and Future of AI Core Concepts
The real question isn’t whether AI will grow—it’s where it will show up next, and how it will change the work you do. Some uses will save time and reduce errors. Others will raise new risks around bias, privacy, and accountability. Knowing the core concepts helps you spot both, so you can adopt AI with confidence instead of reacting to headlines.
AI in Different Industries
AI’s transformative power spans numerous industries, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. It’s a tool and a catalyst for change, inspiring hope for a more efficient and innovative future.
- Healthcare: AI is transforming healthcare through predictive analytics, personalized medicine, and robotic surgeries.
- Finance: In finance, AI algorithms detect fraudulent transactions by analyzing patterns and anomalies in data. AI-driven robo-advisors also provide personalized investment advice, making financial planning more accessible.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles represent the cutting edge of AI in transportation. Companies like Waymo are leveraging AI to create self-driving systems capable of navigating roads, avoiding obstacles, and reducing accidents.
Ethical Considerations
With great power comes great responsibility. The rise of AI brings ethical challenges that need careful consideration.
- Bias and Fairness: AI systems can unintentionally continue biases present in their training data. For example, facial recognition systems have faced criticism for having higher error rates when identifying people of color. Ensuring fairness in AI involves using diverse datasets, such as images of people from different ethnicities, and consistently monitoring for bias.
- Privacy Concerns: AI relies on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data collection, storage, and use. AI developers and policymakers face the crucial challenge of balancing innovation with privacy rights.
- Regulation and Oversight: The rapid pace of AI development calls for robust rules to prevent misuse and ensure accountability. Debates continue over how best to regulate AI without stifling innovation.
Future Trends in AI Core Concepts
Several trends and innovations will shape the future of AI:
- Emerging Technologies: Quantum computing, edge AI, and explainable AI (XAI) are poised to enhance AI’s capabilities. Quantum computing could exponentially speed up data processing. At the same time, edge AI allows real-time data analysis on devices rather than centralized servers, bringing AI’s power closer to the data source.
- Impact on the Job Market: AI core concepts will create new jobs and displace existing ones. Automation might replace routine tasks and open opportunities in AI development, data analysis, and other tech-related fields. Adapting to these changes will require upskilling and reskilling the workforce.
- Predictions for AI Development: Experts predict that AI will continue to advance rapidly, becoming more integrated into various aspects of life. For example, innovations in natural language processing could lead to even more sophisticated virtual assistants and chatbots.
AI core concepts are more than a technological advancement; they are a transformative force reshaping the world. By understanding its core concepts and practical applications, you can appreciate AI’s profound impact, which will continue to have on our lives. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a professional, or just curious about the future, AI offers endless possibilities and challenges worth exploring.
Final Thoughts
AI is no longer something reserved for labs or big tech companies. It’s already embedded in how we work, communicate, create, and make decisions. Understanding AI core concepts—from machine learning and neural networks to deep learning and real-world applications—gives you more than technical knowledge. It gives you context, confidence, and agency in a world where AI increasingly shapes outcomes.
You don’t need to become an engineer to benefit from AI. What matters is knowing what these systems do, how they learn, and where their limits and risks lie. That understanding helps you adopt AI thoughtfully, ask better questions, and use these tools in ways that actually support your goals rather than overwhelm you.
Ready to take the next step and learn how to apply AI core concepts in a practical, beginner-friendly way?
That’s the best next step if you want to move from curiosity to confident, practical use of AI.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Core Concepts
AI core concepts cover how machines mimic human intelligence through learning, reasoning, and problem-solving. They include machine learning, neural networks, deep learning, natural language processing, and computer vision.
Machine learning sits at the center of AI’s core concepts. It lets systems learn from data and improve over time, rather than relying solely on fixed rules.
AI is the broad field of building intelligent systems. Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that trains models to learn from data. Deep learning is a type of machine learning that uses many-layered neural networks to find complex patterns.
AI core concepts explain how everyday tools work—from recommendation engines and virtual assistants to fraud detection and medical imaging. Understanding them helps you use AI more confidently and spot issues like bias and privacy risks.
AI core concepts show up in image recognition, spam filters, speech-to-text, chatbots, recommendation systems, and self-driving cars. All of these rely on machine learning, neural networks, and deep learning applied to different kinds of data.

Florence De Borja is a freelance writer, content strategist, and author with 14+ years of writing experience and a 15-year background in IT and software development. She creates clear, practical content on AI, SaaS, business, digital marketing, real estate, and wellness, with a focus on helping freelancers use AI to work calmer and scale smarter. On her blog, AI Freelancer, she shares systems, workflows, and AI-powered strategies for building a sustainable solo business.


Pingback: Artificial Intelligence for Writers and Creatives - The AI Freelancer